#362: ARK Crypto Brainstorm #2: Crypto Has Been Thriving Amid A Regional Banking Crisis And Macro Uncertainty, & More
1. ARK Crypto Brainstorm #2: Crypto Has Been Thriving Amid A Regional Banking Crisis And Macro Uncertainty

We would like to share the second edition of the ARK Crypto Brainstorm, a quarterly conversation between a rotating group of experts in the crypto space. In this conversation, our esteemed panelists—including Lyn Alden, Jeremy Allaire, Chris Burniske, Angie Dalton, Paul Grewal, Caitlin Long, and Mike Sonnenshein—delved into some of the most pressing topics in the industry, including the current regulatory landscape and the impact of recent regional bank crises on Bitcoin.
Our panelists discussed regulations in the US, particularly the balance between fostering innovation and ensuring consumer protection and the importance of continuing the dialogue between regulators and industry stakeholders. They also explored how the regional bank crisis has elevated Bitcoin as a potentially viable alternative to traditional financial networks as a decentralized and secure store of value not subject to counterparty risk. Additionally, the panelists discussed the promising future of crypto, covering topics like layer-two solutions, DeFi applications, and their potential to shape a more accessible and transparent financial system.
We invite you to watch the full video for a deeper understanding of the panelists’ perspectives and their insights on the current state of crypto.
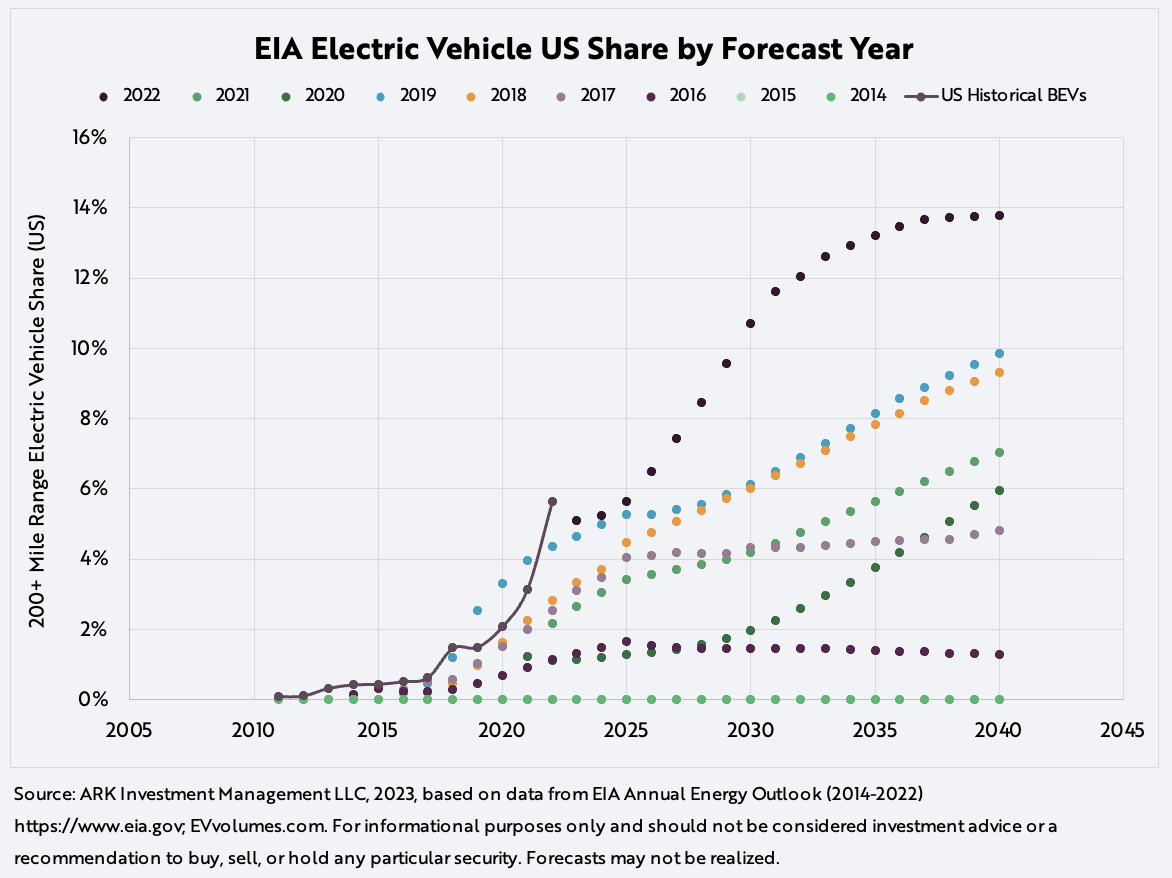
2. The US Energy Information Administration Seems to Have Issues Forecasting Electric Vehicle Sales

In 2014, the US Energy Information Administration (EIA) forecasted that long range electric vehicles (EVs) would have ~0% market share in the US by 2040. Last year, US EV market share topped 5%. Now, having increased its forecast each year, the EIA expect the market share of US EV sales to plateau at ~14% market share in 2040, as shown below. Based on our research, we believe global EV market share is likely to scale to 70%+ by 2027, with the US not far behind.
3. Early Open-Source Projects Are Shaping The Evolution Of AI-Enabled Applications
Recent releases of Auto-GPT and BabyAGI have showcased the significant potential of so-called autonomous agents, sparking considerable excitement across the AI research and software development communities. Built on large language models (LLMs), agents enable LLMs to execute complex sequences of tasks based on user prompts. Equipped with various tools such as internet and local file access, other APIs, and simple memory architectures, these agents demonstrate early progress in the implementation of recursion within AI applications. While still experimental and flawed, we believe agents have the potential to accelerate the productivity gains enabled by AI hardware/software cost declines. According to ARK’s research, AI software could generate up to $14 trillion in revenue and $90 trillion in enterprise value in 2030.
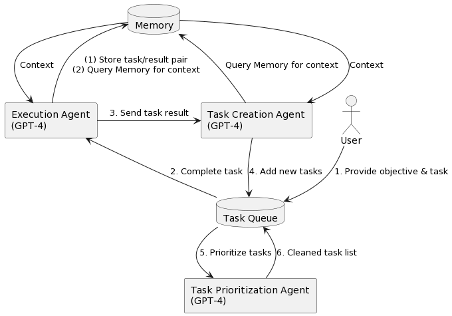
Workflow of an autonomous agent powered by the GPT-4 API.
Source: https://yoheinakajima.com/task-driven-autonomous-agent-utilizing-gpt-4-pinecone-and-langchain-for-diverse-applications/. For informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice or a recommendation to buy, sell, or hold any particular security. Forecasts may not be realized.
Alongside the progress of foundation models such as GPT-4, many companies are training their own smaller, specialized models. While foundation models are useful across a wide variety of use cases, smaller specialized models offer benefits, including lower inference costs. In addition, many companies concerned about copyright issues and data governance are electing to train their own proprietary models with a combination of public and private data. One such example is a 2.7 billion parameter LLM trained on PubMed biomedical data, which achieved positive results on the US Medical Licensing Exam’s (USMLE) question-and-answer test. Training cost only ~$38,000 on the MosaicML platform, with a compute duration of 6.25 days. By comparison, the final training run of GPT-3 is estimated to have cost nearly $5 million in compute.


